Introduction
Understanding the good pH level for garden soil is crucial for every gardener aiming to grow healthy, vibrant plants. Soil pH affects nutrient availability, microbial activity, and overall plant growth. If the soil is too acidic or too alkaline, plants may struggle to absorb the nutrients they need, leading to poor yields and weak growth.
In this article, we will explore the ideal pH range for garden soil, explain how soil pH influences plant health, and provide practical tips on testing and adjusting soil pH. Whether you are growing vegetables, flowers, or fruit trees, mastering soil pH can significantly improve your gardening success.
What Is Soil pH and Why Does It Matter?
Soil pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of soil on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidic soil, while values above 7 indicate alkaline soil.
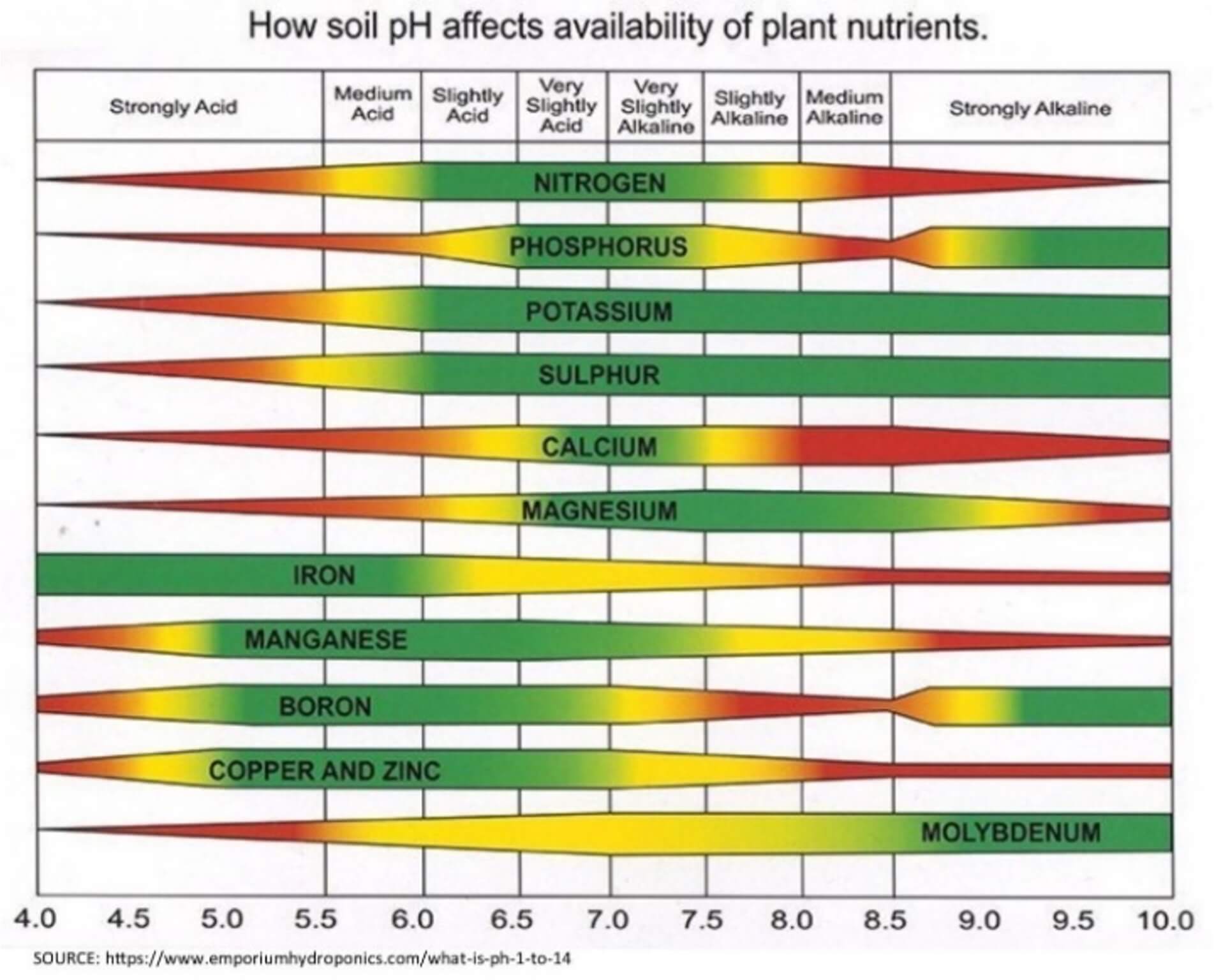
How Soil pH Affects Plant Growth
- Nutrient availability: Most nutrients are most accessible to plants in slightly acidic to neutral soils.
- Microbial activity: Beneficial soil microbes thrive within certain pH ranges, aiding nutrient cycling.
- Toxicity risks: Extreme pH levels can increase toxic elements like aluminum or manganese in the soil.
Understanding these factors helps gardeners maintain the right conditions for optimal plant health.
What Is the Good pH Level for Garden Soil?
Optimal pH Range for Most Garden Plants
The ideal pH level for garden soil typically ranges between 6.0 and 7.0. This range supports:
- Maximum nutrient availability
- Healthy microbial populations
- Strong root development
Variations by Plant Type
Some plants prefer different pH ranges:
- Acid-loving plants: Blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons thrive in soil pH between 4.5 and 5.5.
- Alkaline-tolerant plants: Lavender, asparagus, and clematis grow well in soil pH above 7.0.
Knowing your plant’s pH preference is essential for customizing soil amendments.
How to Test Soil pH Accurately
Accurate soil pH testing is the first step to managing garden soil effectively.
Testing Methods
- Soil test kits: Simple, affordable kits available at garden centers provide quick results.
- pH meters: Digital meters offer precision and are reusable.
- Lab testing: Sending soil samples to a professional lab gives comprehensive analysis.
When to Test
Test soil pH at least once a year, preferably before planting season, to guide soil amendment decisions.
How to Adjust Soil pH for a Healthy Garden
Raising Soil pH (Reducing Acidity)
- Add lime (ground limestone): The most common way to increase pH.
- Use wood ash: Contains potassium and calcium carbonate but apply carefully.
Lowering Soil pH (Reducing Alkalinity)
- Add elemental sulfur: Slowly acidifies soil over time.
- Use organic matter: Peat moss or composted leaves help lower pH naturally.
Tips for Successful pH Adjustment
- Adjust pH gradually; sudden changes can stress plants.
- Retest soil pH after amendments to monitor progress.
- Consider soil texture and drainage, as they influence amendment effectiveness.
Real-World Example: Improving Soil pH for a Vegetable Garden
A homeowner with acidic soil (pH 5.2) wanted to grow tomatoes and peppers, which prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil. After testing, they applied agricultural lime according to soil test recommendations. Over several months, the soil pH rose to 6.5, improving nutrient uptake and resulting in a more productive garden.
Conclusion
Maintaining a good pH level for garden soil—generally between 6.0 and 7.0—is essential for healthy, thriving plants. Soil pH directly influences nutrient availability, microbial health, and plant growth. Testing your soil regularly and adjusting the pH as needed ensures your garden can flourish.
Remember to tailor pH adjustments based on the specific needs of your plants and to make changes gradually. With proper soil pH management, you can unlock the full potential of your garden and enjoy more vibrant, productive plants season after season.