Introduction
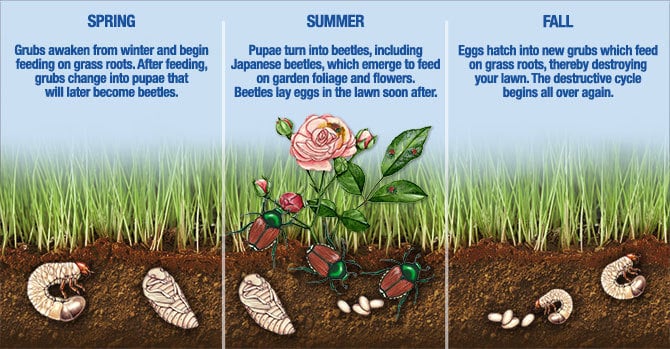
Grubs are a common and destructive pest in gardens worldwide. These white, C-shaped larvae of beetles feed on the roots of grass and plants, causing significant damage that can hinder garden health and growth. Controlling grubs is essential to maintain a lush, thriving garden and prevent long-term soil and plant damage. This article explores proven methods to identify, manage, and prevent grub infestations effectively, ensuring your garden remains healthy and vibrant.
What Are Grubs and How Do They Affect Your Garden?
Grubs primarily consist of larvae from beetle species such as Japanese beetles, June bugs, and chafer beetles. They live underground and consume the roots of grass and plants, leading to symptoms like brown patches, wilting, and weakened plants.
Signs of Grub Infestation
- Irregular brown or dead patches in the lawn
- Spongy soil that lifts easily due to root damage
- Increased presence of animals like birds, skunks, and raccoons digging in the lawn (they feed on grubs)
Recognizing these signs early can help gardeners take timely action to prevent extensive damage.
Natural and Chemical Methods to Control Grubs
Biological Controls
Biological methods offer safe and environmentally friendly options to control grub populations:
- Beneficial Nematodes: Microscopic worms that infect and kill grubs. Apply them to moist soil for best results.
- Milky Spore Disease: A naturally occurring bacterium (Paenibacillus popilliae) that specifically targets Japanese beetle grubs, offering long-term control.
Chemical Treatments
Chemical insecticides such as imidacloprid and chlorantraniliprole are effective against grubs. For optimal results:
- Apply insecticides in late summer or early fall when grubs are small and close to the surface.
- Follow label instructions carefully to protect beneficial insects and the environment.
Cultural Practices to Prevent Grub Damage
Implementing good gardening practices can reduce grub infestations naturally:
- Maintain Healthy Soil: Aerate and fertilize your lawn to promote strong root systems that resist grub damage.
- Proper Watering: Avoid overwatering, which creates favorable conditions for grub development.
- Mowing Height: Keep grass at recommended heights to strengthen root growth.
These measures enhance your garden’s resilience against grub attacks.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Sustainable Control
An IPM approach combines multiple strategies for effective grub control:
- Monitoring: Regularly inspect your lawn for grub presence.
- Threshold Levels: Treat only when grub populations exceed damaging numbers.
- Combination Treatments: Use biological agents alongside cultural practices and targeted chemical applications.
Experts emphasize that IPM reduces chemical use and promotes long-term garden health.
Conclusion
Controlling grubs in your garden requires a balanced approach of identification, prevention, and treatment. By recognizing grub damage early, applying biological or chemical controls thoughtfully, and maintaining healthy garden practices, you can protect your plants and lawn effectively. Embracing an integrated pest management strategy not only controls current infestations but also helps prevent future outbreaks, ensuring your garden remains lush and vibrant year-round. Take action today to safeguard your green space from grub damage!